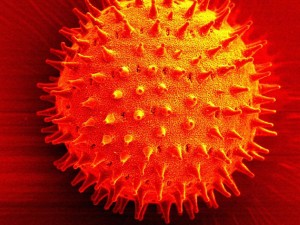
 Pollen season is just around the corner for us here in Washington State. With the warmer than normal temperatures, we will most likely see an early and long pollen season.
Pollen season is just around the corner for us here in Washington State. With the warmer than normal temperatures, we will most likely see an early and long pollen season.
Pollen is a nemesis of rainwater collection and needs to be controlled. Without control, pollen can easily foul our stored water.
As pollen accumulates in cisterns in the spring and summer months, it starts to decay and along with that decay – odor is the result. Simple techniques should be applied in order to keep our stored water “sweet”.
Gutter screens should be cleaned often, as pollen accumulates on the screens themselves with the rain washing the pollen into the gutters and into the cisterns.
Vortex filters screen should be periodically inspected and cleaned as needed. If you do not have a vortex filter, I highly recommend having one installed.
If you use screen baskets in a sump box or the cistern itself, a layer of cheesecloth will catch the pollen before it enters the tank. The cheesecloth should be inspected frequently and replaced as needed.
Keep your stored water clean and odor free with a little extra maintenance during this pollen season. You will be glad you did.
A false color electron microscope scan of pollen. Credit: Dartmouth College/Charles Daghlian


 Rainwater collection, a simple source for decentralized water, can be the answer to our aging, centralized water systems. With expected increased demand from high density development and the high cost of upgrading infrastructure to meet those demands, water will become the new commodity. Much has been discussed about privatization of water districts in order to fund these expenses, turning these districts into “for profit” businesses. Large corporations such as
Rainwater collection, a simple source for decentralized water, can be the answer to our aging, centralized water systems. With expected increased demand from high density development and the high cost of upgrading infrastructure to meet those demands, water will become the new commodity. Much has been discussed about privatization of water districts in order to fund these expenses, turning these districts into “for profit” businesses. Large corporations such as 
 How much is water worth?
How much is water worth?