 There has been a great deal of inquiry about sole source use of rainwater collection in King County, causing confusion for the public – as well as for King County public officials. RainBank is currently consulting on four different projects, assisting clients with navigating the system.
There has been a great deal of inquiry about sole source use of rainwater collection in King County, causing confusion for the public – as well as for King County public officials. RainBank is currently consulting on four different projects, assisting clients with navigating the system.
A change in Department of Public Health Policy, which is the authority on single source rainwater collection, has been transferred back to the Onsite Sewage System Authority (OSS) of King County Public Health.
There is a section of Title 13 that refers to rainwater collection for single source usage. This authority has jurisdiction over sole source use; any other permitting approval for supplementary source is to be approved by King County Public Health Department’s senior plumbing inspectors. There are plumbing codes that must be met with regard to installation and permitting from KCH plumbing division for any RWC system that is potable or non potable, that is connected to household plumbing.
Below is the section of Title 13 dated November 20, 2013, which refers to sole source usage
D. A rainwater catchment system that serves as the only source of drinking water for a single family residence and that complies with each of the following conditions:
1. The health officer finds that requiring connection of the plumbing system to an approved public water source or to an approved private well would cause undue hardship.
2. Application for a rainwater catchment system source approval shall be submitted for review on forms provided by the health officer. The applicant shall pay to the health officer the rainwater catchment system review fee as specified in the fee schedule, payable after completion of the application review.
3. Application for a rainwater catchment system source approval shall be prepared by any one or more of the following:
a. A professional engineer authorized under a current, valid license to practice in Washington state;
b. An environmental health professional holding a current, valid registration from either the Washington State Environmental Health Association or the National Environmental Health Association;
c. A King County licensed water system designer holding a current, valid license to design water systems in King County; and
d. A rainwater system designer holding a current, valid accreditation from the American Rainwater Catchment System Association.
4. Rainwater catchment system source design shall conform to Part III of Chapter 16 of the Uniform Plumbing Code, 2009 edition, as amended, and shall include, at a minimum, the following information:
a. Estimated daily and weekly and annual demand;
b. Available catchment area and estimated annual rainwater capture;
c. Roofing materials used;
d. Storage capacity of and materials used in the construction of the rainwater catchment system; e. treatment specifications including filtrations and disinfection system specifications; and
f. Operation and maintenance requirements.
5. Composite or shake shingles or other materials determined by the health officer to present a risk of contamination may not be approved or used as roofing materials for a rainwater catchment system source.
6. Before using a rainwater catchment system source, the property owner shall file in the county recorder’s office a notice on title advising that the property is served by a rainwater catchment system and including the following information:
a. The estimated daily, weekly and annual water supply furnished by the rainwater catchment system;
b. That the water supply from the rainwater catchment system may be limited due to variations in rainfall or usage; and
c. That regular maintenance of the treatment system and components is required in order to minimize the risk of consuming contaminated water.
As rainwater collection becomes less of a niche and more mainstream for residential and commercial applications, and with 15 years of design and installation experience, RainBank is the go-to source and your advocate for rainwater collection systems in the Pacific Northwest. Using the form below, contact us today to learn how we can help you with proper system design, installation and consultation through the sometimes confusing permitting requirements for potable, non-potable, sole source and supplementary systems in and around Seattle, Washington state and beyond.


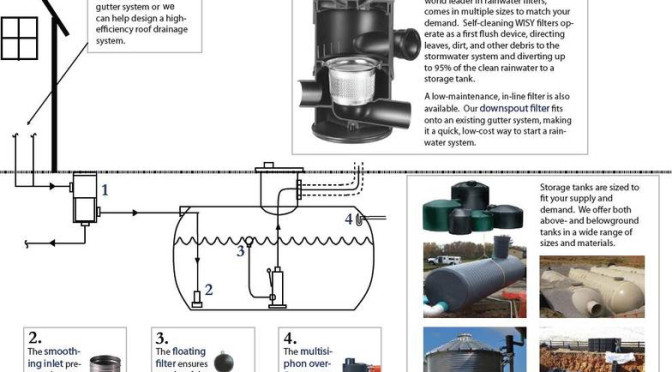
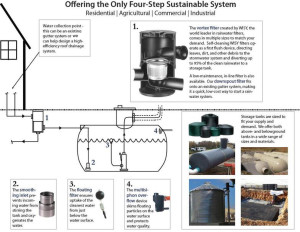

 Although it is fairly clean at the outset, when it comes in contact with impure surfaces, rainwater may need some treatment before drinking. A rainwater collection system designed with filtration and disinfection will get the job done.
Although it is fairly clean at the outset, when it comes in contact with impure surfaces, rainwater may need some treatment before drinking. A rainwater collection system designed with filtration and disinfection will get the job done.