 In order to establish usage for a rainwater collection system annual, monthly, and daily rainfall amounts, along with water usage demands need to be taken into consideration.
In order to establish usage for a rainwater collection system annual, monthly, and daily rainfall amounts, along with water usage demands need to be taken into consideration.
Current water use is informative to help with sizing a system, but future demands should be considered as well. Growing family, guests, possible resale of the house should be accounted for. The system should be designed and built with upgrades for the future in mind, allowing for the system to supply what the future may hold.
Possible drought or longer periods of dry season should also be considered when designing or building a system. Incorporating back up water supplies into a system can be as easy as hauled water, or drawing from a well, community or city water system and should be an available option for those times. Residential rainwater systems in the city are often limited in space for storage, leaving the volume of the cisterns inadequate for year round use. Having the ability to switch to this alternate source can be a necessity in design. However, a more rural environment lends itself to larger storage capacities.
Water demand is an important part of design and the American Water Works Association (AWWA) has conducted a study of various fixtures and appliances. Knowing these demands will help estimate usage and assist the designer to adapt the design accordingly. Single flush toilets use 1.28 gal/ flush, dual flush toilets 1.0 gal/ flush for liquids and 1.28 gal/ flush for solid. Average use is 6 flushes per person, per day. Low use fixtures such as shower heads, faucets, cloths washer (front loading) are recommended for the overall design of the house and can be found in publications from manufacturers.
Outdoor demand should be limited as much as possible. Drought tolerant plantings, drip irrigation, and general conservation will help limit outdoor usage.
For specific irrigation needs, Evapotranspiration (ET) is the measurement of amount of water in inches that is needed to grow plants. All plants have a different watering requirements, also being affected by temperature, wind, humidity, and sunlight. A state climatologist can be contacted to attain an ET standard reference for your area. Careful consideration of outdoor use must be given if irrigation is part of the RWC design. An average city lot can use as much as 1,800 gallons of water for watering a lawn.
In order to get the best performance from your rainwater collection system, indoor and outdoor demands must be carefully calculated using best storage capacities, surplus and defect, level of storage, daily, monthly, and annual use/demand for the entire year. Simply calculating the average annual rainfall amounts will not produce the end goal of a well designed RWC system. It is best to determine average potential of collection and use. Determine average daily, monthly, and annual rainfall amounts. Calculate collection area, and determine runoff. Identify highs and lows of rainfall amounts and demands. Determine those months of low amounts of rainfall along with the carryovers from months prior. Certainly, identify those months of zero rainfall.
Know your consumption of current and future use. Use water efficient fixtures and practice conservation. Understand that during those times of low amounts of rainfall, you may need to “tighten the belt a bit” or switch to the alternate source. Determine your desires and demands during the planning stage by doing so your system will produce the results you are looking for.
 The American Rainwater Catchment Systems Association, ARCSA, is a driving force in placing rain harvesting in the national spotlight by petitioning President Obama’s administration to focus on the broad economic value of supporting and encouraging growth in the rainwater harvesting industry.
The American Rainwater Catchment Systems Association, ARCSA, is a driving force in placing rain harvesting in the national spotlight by petitioning President Obama’s administration to focus on the broad economic value of supporting and encouraging growth in the rainwater harvesting industry.


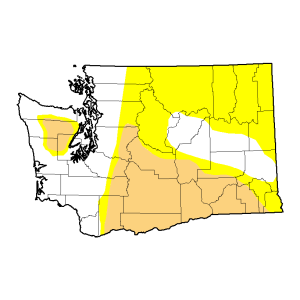 Snow pack in the Cascades is 7-50% of normal and the Olympics at only 7% at the end of March. The US Drought Monitor shows that the affected areas of “abnormally dry” is the North Eastern part of the state with the South Eastern being “moderately dry” while the Olympics are at “moderately dry”.
Snow pack in the Cascades is 7-50% of normal and the Olympics at only 7% at the end of March. The US Drought Monitor shows that the affected areas of “abnormally dry” is the North Eastern part of the state with the South Eastern being “moderately dry” while the Olympics are at “moderately dry”.
 In order to establish usage for a rainwater collection system annual, monthly, and daily rainfall amounts, along with water usage demands need to be taken into consideration.
In order to establish usage for a rainwater collection system annual, monthly, and daily rainfall amounts, along with water usage demands need to be taken into consideration.